What do we put in space?
What do we put in space?
Space technologies are being put up by a host of government and non-government actors now jockeying for space in space. In the 21st century, space has become an increasingly democratized environment. More countries, non-state actors, international organizations, and corporations are harnessing space capabilities and employing them in a myriad of ways. Civilian government organizations, such as NASA and NOAA, use satellites to keep track of changing climates, monitor natural disasters, and take images of far-away galaxies. Military uses of satellites include reconnaissance, navigation, and communications. Commercial industry deploys satellites to provide a variety of services, including satellite television and navigation, and are using innovative space technologies to provide internet and cell phone coverage across the globe. As if that wasn’t enough, innovations in satellite designs have allowed for smaller satellites to be put into orbit at lower cost, making space more accessible to a larger number of satellite operators.
Can current systems adapt to address the challenges that arise from the growing number of CubeSats, a class of satellites that are small and low-cost yet have emerging concerns?
Learn moreTechnical standards were key to accelerating the initial development of CubeSats. But CubeSats’ impact on research and education is contingent on regulatory standards that are accessible to new players in space exploration.
Learn more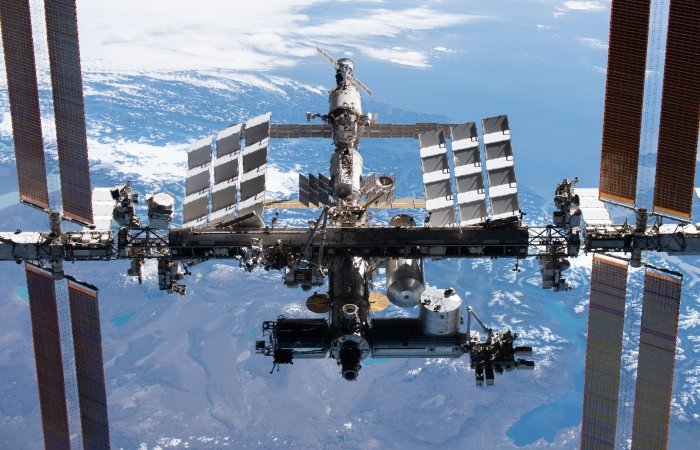
NASA Looks to Private Sector for Successor to the International Space Station
For more than 20 years, the ISS has served as a continuously inhabited foothold in low Earth orbit, a way for space agencies around the world to study how humans live off the Earth for extended periods. But it's not clear how long this will last. Written by Christian Davenport.
Learn more
The Global Legal Landscape of Space: Who Writes the Rules on the Final Frontier?
We no longer need a telescope to see the critical importance of space. But while much attention has been paid to the geostrategic and economic significance of space, perhaps the most foundational area has been largely left on the backburner: space governance. The current global space governance framework has been slow to take evolving state and industry practices as well as technological changes into consideration, namely around issues of celestial resource use and space militarization.
Read moreSatellites will play a key role in determining our collective 5G future. How we integrate terrestrial and space-based components will determine the type and degree of connectivity 5G networks enable in practice across the United States and around the world, rather than what they could have enabled in theory.
Learn moreMuch of the world’s critical infrastructure is heavily dependent on space, specifically space-based assets, for its daily functioning. This dependence poses a serious, and yet frequently underrecognized, security dilemma -- especially cyber threats -- for critical infrastructure providers and policymakers alike.
Read more on CTRL Forward